Tutorial 1: Poisson Equation in 1D
As a starting point we use the Poisson equation on the unit interval with Dirichlet boundary conditions, i.e. we consider the following equation:
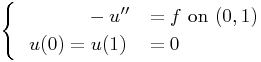
The solution is obtained using a uniform Wavelet-Galerkin method utilizing a diagonal preconditioner. This results in the following code:
*
* This example calculates a poisson problem with constant forcing f on the
* one-dimensional domain [0,1], i.e.
* - u'' = f on (0,1) , u(0) = u(1) = 0.
* The solution is obtained using a uniform Wavelet-Galerkin method with a
* diagonal scaling preconditioner.
*/
First we simply include the general LAWA header lawa/lawa.h for simplicity, thus having all LAWA features available. All LAWA features reside in the namespace lawa, so we introduce the namespace lawa globally.
#include <fstream>
#include <lawa/lawa.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace lawa;
Several typedefs for notational convenience.
Typedefs for Flens data types:
typedef flens::GeMatrix<flens::FullStorage<T, cxxblas::ColMajor> > FullColMatrixT;
typedef flens::SparseGeMatrix<flens::CRS<T,flens::CRS_General> > SparseMatrixT;
typedef flens::DiagonalMatrix<T> DiagonalMatrixT;
typedef flens::DenseVector<flens::Array<T> > DenseVectorT;
Typedefs for problem components:
Primal Basis over an interval, using Dijkema construction
HelmholtzOperator in 1D, i.e. for 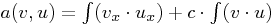
Preconditioner: diagonal scaling with norm of operator
Right Hand Side (RHS): basic 1D class for rhs integrals of the form 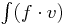 , possibly with additional peak contributions (not needed here)
, possibly with additional peak contributions (not needed here)
Forcing function of the form T f(T x) - here a constant function
rhs_f(T x)
{
return 1.;
}
Auxiliary function to print solution values, generates .txt-file with columns: x u(x)
printU(const DenseVectorT u, const PrimalBasis& basis, const int J,
const char* filename, const double deltaX=1./128.)
{
ofstream file(filename);
for(double x = 0; x <= 1.; x += deltaX){
file << x << " " << evaluate(basis,J, u, x, 0) << endl;
}
file.close();
}
int main()
{
wavelet basis parameters:
int d_ = 2;
int j0 = 2; // minimal level
int J = 5; // maximal level
Basis initialization, using Dirichlet boundary conditions
basis.enforceBoundaryCondition<DirichletBC>();
Operator initialization
DiagonalPrec p(a);
Righthandside initialization
FullColMatrixT deltas; // peaks (and corresponding scaling coefficients): here none
Function<T> F(rhs_f, singPts); // Function object (wraps a function and its singular points)
Rhs rhs(basis, F, deltas, 4, false, true); // RHS: specify integration order for Gauss quadrature (here: 4) and
// if there are singular parts (false) and/or smooth parts (true)
// in the integral
Assembler: assemble the problem components
SparseMatrixT A = assembler.assembleStiffnessMatrix(a, J);
DiagonalMatrixT P = assembler.assemblePreconditioner(p, J);
DenseVectorT f = assembler.assembleRHS(rhs, J);
Initialize empty solution vector
Solve problem using pcg
x Print solution to file "u.txt"
printU(u, basis, J, "u.txt");
return 0;
}
